Map of VUB Campus Etterbeek
If you wish to come by car, please register your license plate here, several days in advance, and write coen.de.roover@vub.be as the email address of the "host". You can then use any of the parking facilities at the VUB.
5 December 2025
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
- Location
-
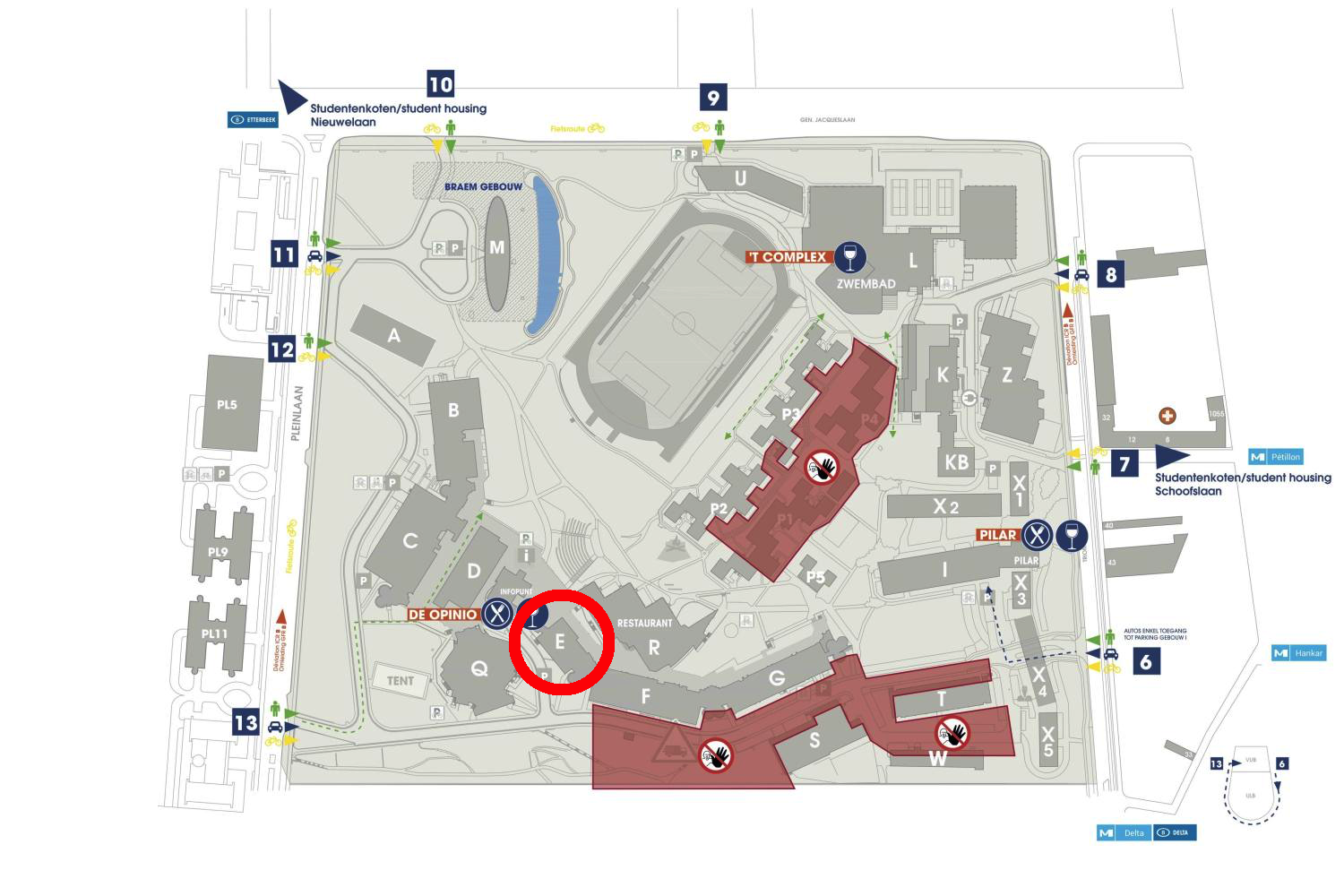
Room E.0.04, Building E
Campus Etterbeek, Vrije Universiteit Brussel
Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussel
- 12:30 - 13:00
- Welcome lunch with sandwich
- 13:00 - 16:30
-
Advisory board meeting and presentations:
-
13:00 - 13:15 – Welcome
13:15 - 14:00 – Keynote-
"Fuzzing Web APIs in Industry with EvoMaster"
Prof. Andrea Arcuri
(Abstract and Bio below)
-
Resilience Testing
Failure Reproduction (Piloted at KatoenNatie)
** Coffee break **
Flakey Tests (Piloted at Nokia)
Test Amplification (Piloted at KatoenNatie)
-
Quest for additional pilot projects next year
- 16:30 - ...
- Reception with networking drink
Keynote: "Fuzzing Web APIs in Industry with EvoMaster"
Abstract:
As researchers in academia, we have worked for the last 9 years on the open-source fuzz-testing tool called EvoMaster. A fuzzer is able to automatically generate test cases, automatically finding different types of faults. In the case of EvoMaster, we can automatically generate test cases for REST APIs (as well as GraphQL and RPC), with output test suites in different formats such as Python or Java. Faults that are found are based for example on HTTP 500 status code (server error), mismatches between the API responses and what declared in their OpenAPI schema, and different kinds of security related properties that are not satisfied.
In our work, we have been pushing forward the state-of-the-art in AI research for software testing. But are those techniques actually useful for test practitioners? What important aspects are missing or neglected?
In this talk, we will discuss in more details our collaboration/engagement with test engineers at Fortune 500 enterprises such as Volkswagen in Germany and Meituan in China. We share the experience on how testers have been using this kind of tool to simplify their work.
Anyone can download and use an open-source tool such as EvoMaster. However, industry-academia collaborations are important for academics to get access to real-world systems, whereas the practitioners benefit from feature-requests/bug-fixing prioritization.
Short bio:
Prof. Andrea Arcuri is a Professor of Software Engineering at Kristiania University College and Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway.
His main research interests are in software testing, especially test case generation using AI techniques. Having worked 5 years in industry as a senior engineer, a main focus of his research is to design novel research solutions that can actually be used in practice. Prof. Arcuri is the main-author of EvoMaster and a co-author of EvoSuite, which are open-source tools that can automatically generate test cases. He received his PhD in search-based software testing from the University of Birmingham, UK, in 2009.

If you wish to come by car, do not forget to register your license plate via the link you received by email!
26 September 2024
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
- Location
-
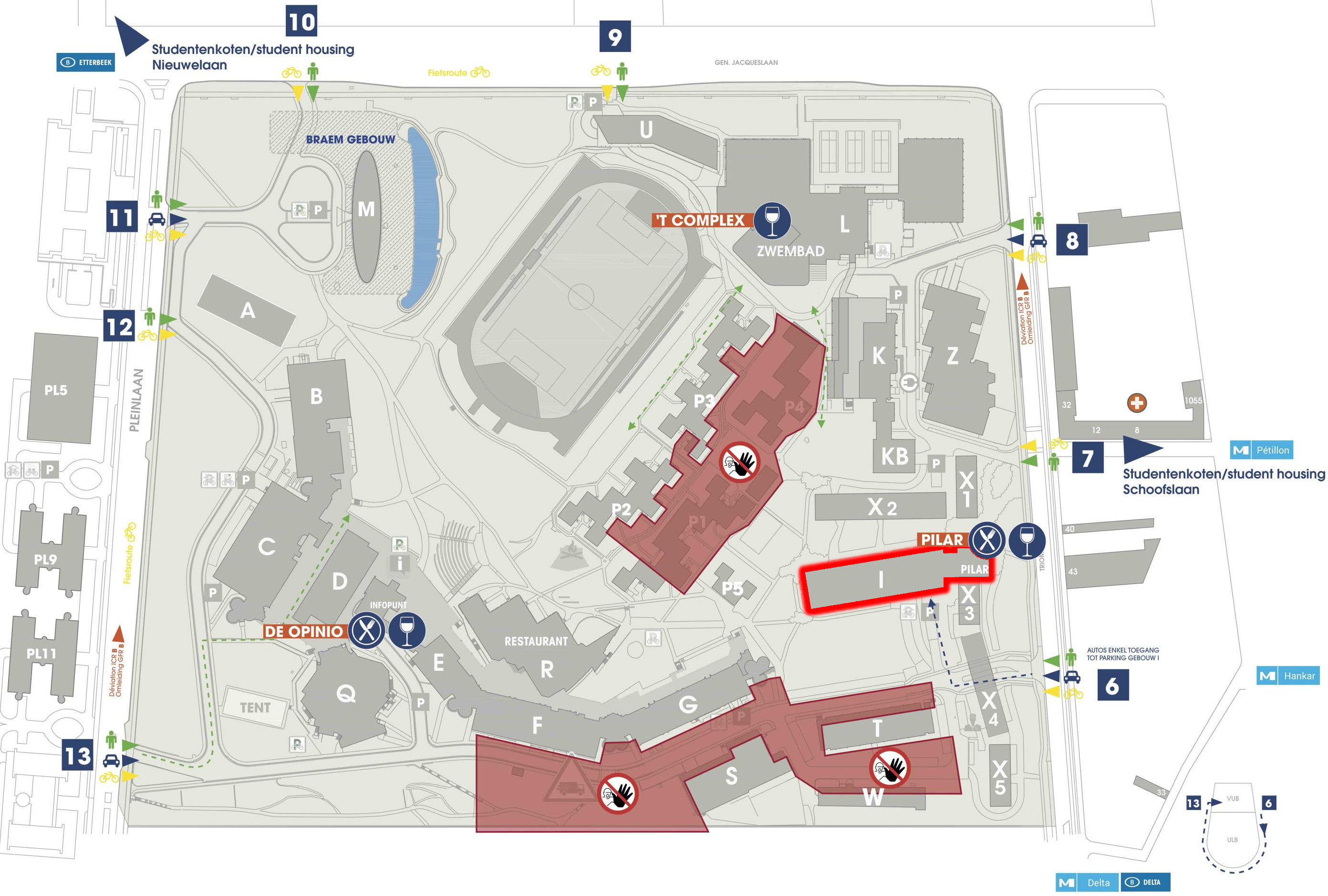
Room I.2.01, Building I
Campus Etterbeek, Vrije Universiteit Brussel
Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussel
- 12:30 - 13:00
- Welcome lunch with sandwich
- 13:00 - 16:30
-
Advisory board meeting and presentations:
- Discuss project progress
- Set-up pilot projects
-
Keynote by Annibale Panichella (TU Delft):
Title: AI-Based Testing for the Testing Pyramid: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract: Nowadays, Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a critical role in automating different human-intensive tasks, including software engineering tasks. Since the late 1970s, researchers have proposed automated techniques to generate test data (fuzzing) or unit-level test suites (test suite generation) automatically. Proposed techniques span from simple heuristics to more advanced AI-based techniques and evolutionary intelligence. This talk will cover our recent works in this field with particular attention to industrial domains, including integration testing, compiler fuzzing, and emerging cyber-physical systems. The talk will also highlight open challenges and research opportunities for AI-based testing.
Bio: Annibale Panichella is an Associate Professor in the Software Engineering Research Group (SERG) at Delft Universtiy of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands. Within SERG, he leads the Computation Intelligence for Software Engineering Lab (CISELab), where his research focuses on advancing the fields of software testing, search-based software engineering, software testing for AI, and empirical software engineering. He is the track lead for “Testing for and with AI” at the AI4SE, TU Delft’s tenth ICAI lab, funded by JetBrains, a global leader in intelligent software development tools. Additionally, he is the principal investigator for the UBRI program at TU Delft, a pioneering joint initiative with Ripple, a leader in the Blockchain sector. He served as a program committee member for prestigious international conferences such as ICSE, ESEC/FSE, ASE, ISSTA, GECCO, and ICST, and as a reviewer for leading journals including TSE, TOSEM, TEVC, EMSE, and STVR.
- 16:30
- Reception with networking drink in room F.10.729
2 February 2024
UAntwerpen
- Location
-
Room CMI G.004
UAntwerpen, Campus Middelheim
Middelheimlaan 1, 2020 Antwerpen
- 12:30 - 13:00
- Welcome with sandwich lunch
- 13:00 - 16:30
-
Advisory board meeting:
- Discuss project progress
- Set-up pilot projects
-
Keynote by Burcu Özkan (TU Delft):
Testing Distributed System Implementations
Almost all software systems we develop and use today are distributed. While distributed software systems provide scalability and improve performance, they are hard to implement correctly. The programmers need to reason about the concurrency in the executions of the distributed components, asynchrony in their communication, and possible component or network failures. Testing distributed systems under different execution scenarios is a practical solution for detecting bugs in their implementations. This talk will discuss the challenges of testing distributed system implementations, key ideas in our testing techniques, and their applications to large-scale systems.
- 16:30
- Reception with networking drink


If you wish to come by car, do not forget to register your license plate via the link you received by email!
6 June 2023
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
- Location
-
Room I.0.01, Building I
Campus Etterbeek, Vrije Universiteit Brussel
Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussel
- 12:00 - 13:00
- Welcome lunch with Bao Buns in "Bar Pilar"
- 13:00 - 16:30
-
Advisory board meeting and presentations:
- Testing Cloud-Native: A Journey from Open-Source Applications to Industrial Pilot Studies
- Testing the Resilience of Cloud-Native Applications: Proof of Concept
- Discovering & Inducing Flaky Tests
-
Keynote by Mika Mäntylä (University of Oulu):
Beyond Pass/Fail and Grepping: Classical Computing Solutions for Root Cause Analysis in Test Automation
Test automation should move from pass/fail analysis to identify the root causes of test failures. In the face of vast volumes of log data generated by test cases, industry professionals traditionally resort to their domain knowledge to construct 'grepping' keywords for sifting through log files. Recently, the academic community has proposed deep-learning for log anomaly detection. However, deep-learning can often be complex and costly to train. In this talk, we make a case for classical computing solutions. With their simplicity and efficiency, classical computing may be a more practical and feasible starting point for advancing the industry in analyzing test failures.
- 16:30
- Reception with networking drink
23 January 2023
UAntwerpen
- Location
-
Room CMI G.017
UAntwerpen, Campus Middelheim
Middelheimlaan 1, 2020 Antwerpen
- 12:30 - 13:00
- Welcome with sandwich lunch
- 13:00 - 16:30
-
Advisory board meeting:
- Practical matters
- Introduction to the project
- Questions to the Advisory Board
- Keynote by Xavier Devroey (UNamur): Highly Contextual Search-based Test Case Generation
- 16:30
- Reception with networking drink in room F.10.729